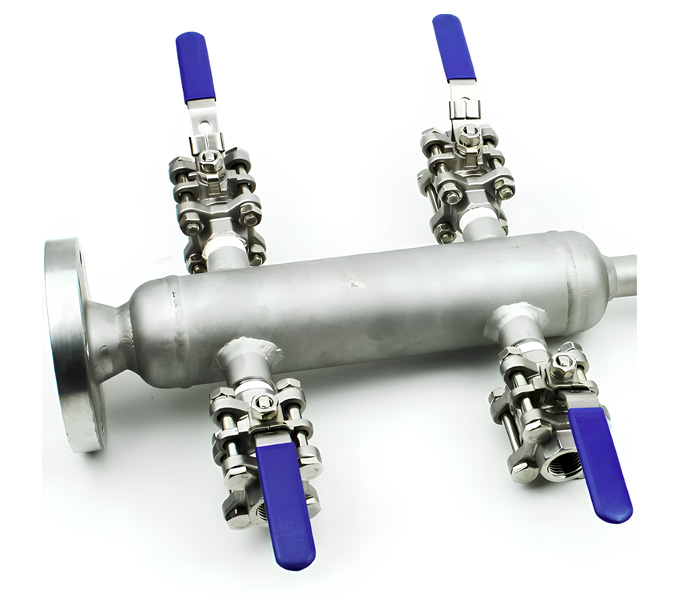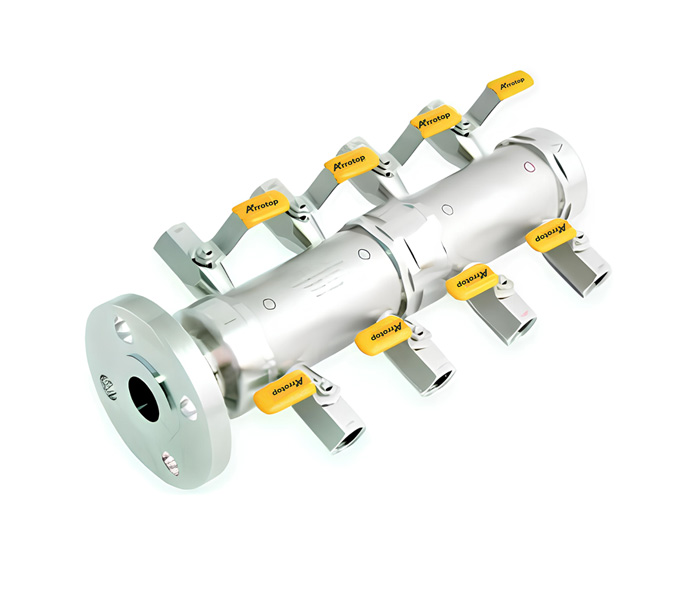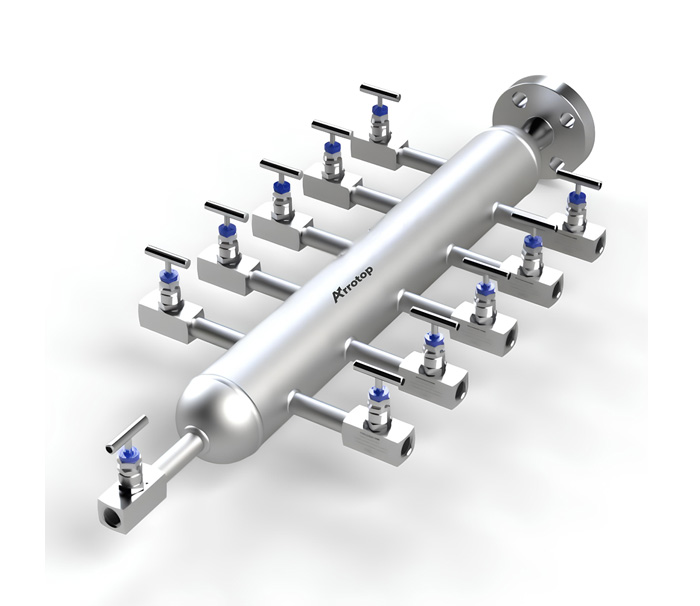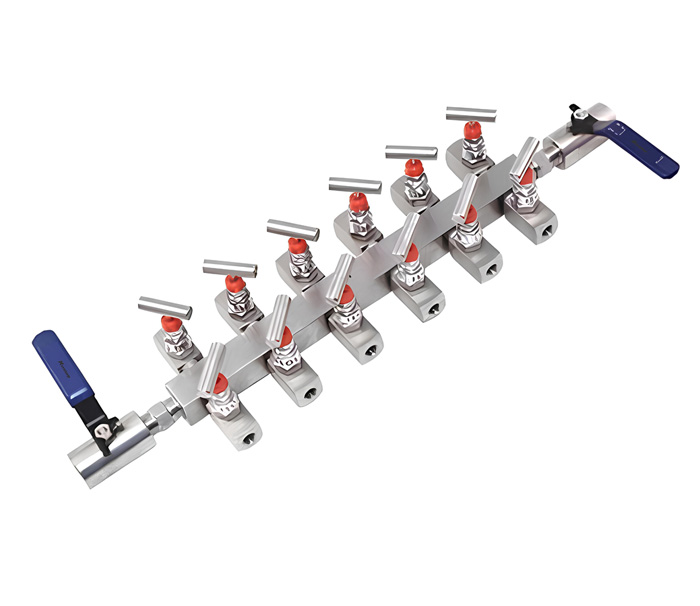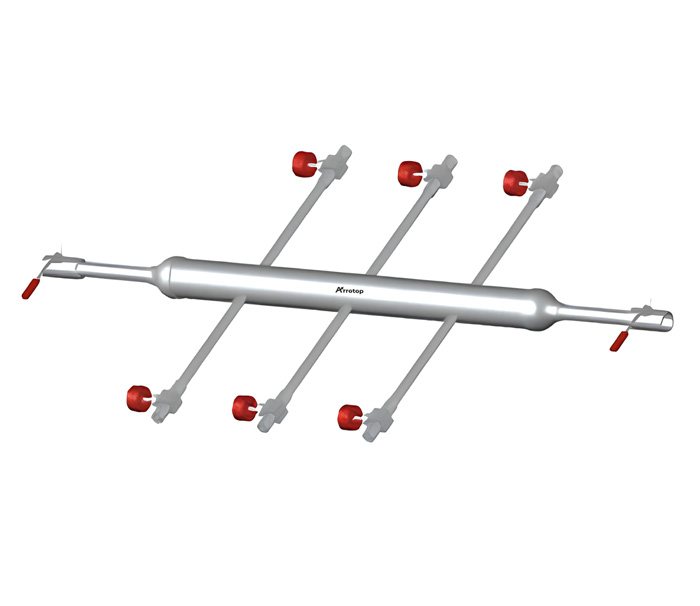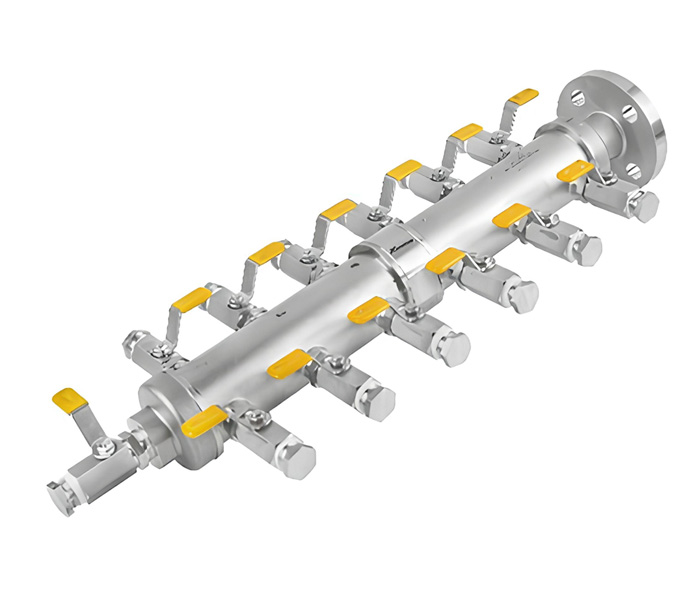
What are Air Headers?
Arrotop’s Air headers are components used in industrial processes, particularly in systems that involve the control and distribution of air or gases. These headers play a crucial role in managing the flow of compressed air or other gases within a system. The term “header” is often used to refer to a manifold or a distribution system that collects and distributes the air or gas to various points in the system.
Arrotop’s air headers offer reliable and efficient solutions for distributing compressed air tailored to meet the demands of various industrial applications. With a focus on quality and innovation, Arrotop delivers products that ensure superior performance and longevity.
Types of Air Headers
Product Data
Arrotop’s air headers are designed to provide a reliable and efficient means of distributing compressed air in industrial systems. These headers are engineered for durability, versatility, and ease of maintenance, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Air headers play a critical role in ensuring the smooth operation of pneumatic systems by distributing compressed air from a single source to multiple destinations.
Design and Construction
Body Material Options :
- 316/L Stainless Steel
- 304/L Stainless Steel
- Carbon Steel
- Alloy Steel
- Other alloys available upon request
Connections: Multiple outlet connections, customizable based on application requirements.
Sizes: Standard and custom sizes available.
Performance
- Pressure Rating: Up to 6000 psi (410 bar)
- Temperature Rating: -20°F to 800°F (-29°C to 427°C)
- Flow Characteristics: Optimized for minimal pressure drop
- Standards Compliance: ASME, API, ISO, and other relevant standards
Model Numbers for Arrotop Air Headers
| Model Number | Description |
|---|---|
| AAH150-4 | Air header, 4-way, up to 150 psi |
| AAH300-6 | Air header, 6-way, up to 300 psi |
| AAH600-8 | Air header, 8-way, up to 600 psi |
| AAH1500-10 | Air header, 10-way, up to 1500 psi |
| AAH2500-12 | Air header, 12-way, up to 2500 psi |
| AAH6000-16 | Air header, 16-way, up to 6000 psi |
Key Features
- Durability: Constructed from high-quality materials to ensure long-lasting performance in harsh environments.
- Efficiency: Designed to distribute compressed air with minimal pressure drop.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
- Ease of Maintenance: Accessible design for easy servicing and maintenance.
- Safety: Equipped with overpressure safety valves to release excess pressure.
- Customizability: Custom designs to meet specific application requirements.
Technical Information
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Pressure Rating | Up to 6000 psi (410 bar) |
| Temperature Rating | -20°F to 800°F (-29°C to 427°C) |
| Body Material | 316/L, 304/L, Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, other alloys on request |
| Connections | Multiple outlet, customizable |
| Sizes | Standard and custom sizes available |
| Standards Compliance | ASME, API, ISO, and other relevant standards |
| Mounting Options | Wall-mounted, floor-mounted, or customized mounting solutions |
| Valve Options | Integral valves, ball valves, needle valves, or globe valves |
| Manifold Configurations | Customizable configurations for different outlet requirements |
| Surface Finish | Available in various finishes including polished, painted, or coated |
Applications of Air Headers:
- Manufacturing Industry: Air headers are widely used in manufacturing processes for powering pneumatic tools, controlling actuators, and providing air for various automated systems. They play a crucial role in the operation of production lines, ensuring efficient and reliable performance of machinery.
- Petrochemical Industry: In the petrochemical sector, air headers are utilized for tasks such as pneumatic conveying, controlling valves and actuators, and supplying air to instrumentation and control systems. They contribute to the safe and efficient operation of processes in refineries and chemical plants.
- Power Plants: Air headers are employed in power plants for tasks like controlling pneumatic valves, operating actuators, and providing air for combustion processes. They help ensure the proper functioning of various components within the power generation system.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: In pharmaceutical manufacturing, air headers play a role in providing clean and controlled compressed air for processes such as tablet coating, packaging, and pneumatic conveying. The stringent requirements for cleanliness and precision make air headers valuable in pharmaceutical facilities.
- Automotive Industry: Air headers are used in the automotive sector for tasks such as operating pneumatic tools, controlling robotic systems, and managing air supply for paint booths. Their role in providing reliable and regulated compressed air contributes to the efficiency of manufacturing processes.
- Food and Beverage Industry: In food processing plants, air headers are employed for tasks such as controlling pneumatic actuators, powering conveyors, and managing packaging systems. The clean and regulated air supplied by air headers is crucial in maintaining the quality and hygiene standards of the food and beverage industry.
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: Air headers are utilized in water treatment facilities for tasks such as aeration in biological treatment processes, controlling valves, and operating pneumatic equipment. They contribute to the efficient treatment of water and wastewater.
- Mining Industry: In mining operations, air headers are employed for tasks such as operating pneumatic drills, controlling valves in processing plants, and providing air for underground ventilation systems. Their robust design and reliability are important in challenging mining environments.
- Instrumentation and Control Systems: Air headers play a key role in supplying compressed air to pneumatic instruments and control systems across various industries. They ensure the proper functioning of instruments that rely on compressed air for measurement and control.
Advantages of Air Headers:
- Centralized Distribution: Air headers allow for the centralized distribution of compressed air or gases from a single source to various points within a system. This simplifies the overall system design and reduces the need for multiple individual connections.
- Efficient Operation: By using air headers, it becomes easier to control and regulate the flow of air or gases to different sections of a process. This efficiency is crucial for maintaining optimal operating conditions and ensuring that each component of the system receives the required amount of air at the correct pressure.
- Pressure Regulation: Air headers often include pressure regulators that help maintain a consistent pressure throughout the system. This is important for ensuring the proper functioning of equipment and instruments that rely on specific pressure levels.
- Isolation and Maintenance: Air headers incorporate valves that allow for the isolation of specific sections or equipment within the system. This feature is advantageous for maintenance purposes, as it enables technicians to work on a particular part of the system without affecting the entire process.
- Instrumentation: Air headers can be equipped with various instruments, such as pressure gauges, temperature sensors, and flow meters, providing operators with real-time data on the conditions of the air or gases within the system. This monitoring capability is crucial for maintaining control and identifying potential issues.
- Safety Features: Some air headers come with safety features, including relief valves, which help prevent overpressure situations. These safety measures contribute to the overall safety of the industrial processes and protect both equipment and personnel.
- Flexibility: Air headers are designed to be versatile, allowing for modifications and expansions in the system as needed. This flexibility is valuable in industries where processes may change or grow over time.
- Cost-Effective: The centralized distribution and control provided by air headers can lead to cost savings in terms of both equipment and maintenance. The streamlined design reduces the complexity of the system, making it more straightforward to install, operate, and maintain.